Termite
The egg-laying termite queen lays her eggs, the termite larvae transform into termite workers, termite soldiers or reproductive termites.
Dampwood Termites
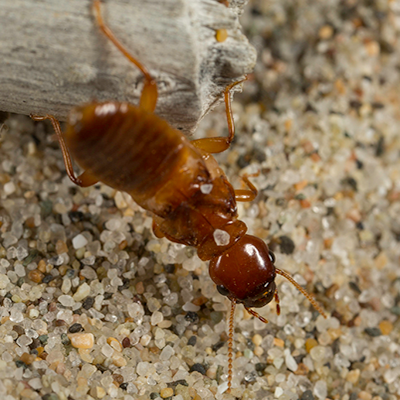
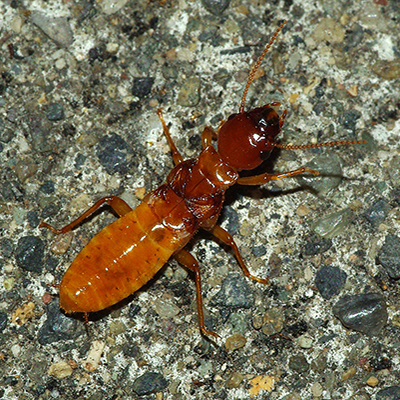
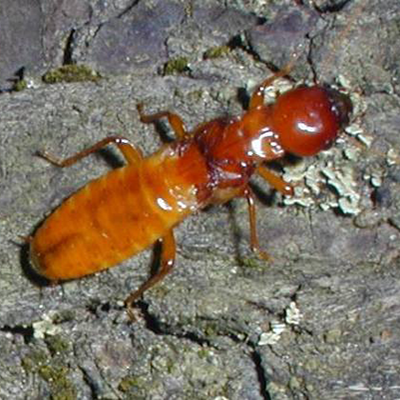



Dampwood termites like to live and feed in very moist wood. because they need lots of moisture, Dampwood Termites usually live in damp, dying wood or in houses with leaking plumbing that keeps the wood wet.Dampwood termites do not carry disease and don?t usually bother buildings because there is not enough water in the wood. To avoid Dampwood termites, make sure water drains away from your house and keep damp wood away from your home.
Drywood termites
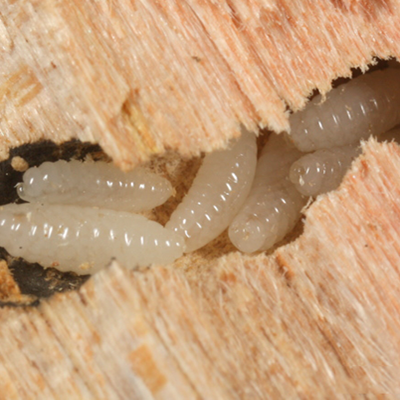
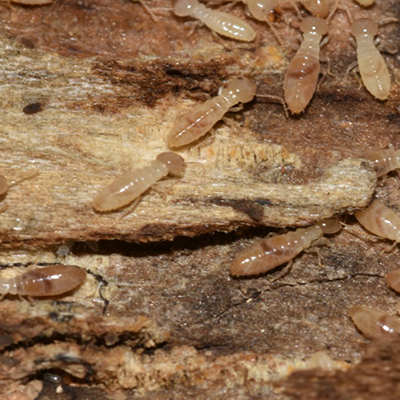
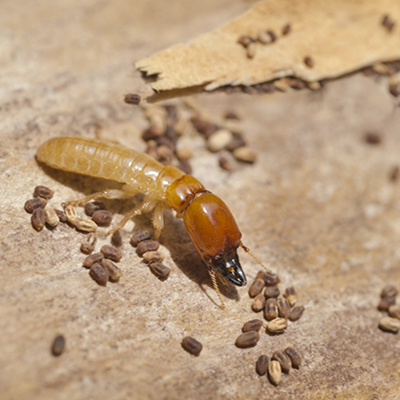



Drywood termites form colonies of up to 2,500 members. Drywood Termite colonies don?t have workers. Younger termites, called "false workers", do all the work for the colony. Drywood Termites eat wood, wallpaper, plastics and fabric made from plants. Drywood Termite colonies are usually found in dry wood and they do not require moisture or contact with the soil.Drywood termites can build nests and dig tunnels in buildings. These tunnels cause major damage because the wooden support beams can become weak and make the building lean or fall down. To Prevent your Home from Drywood Termite, make sure firewood and scrap wood is stored away from your house. Seal all cracks and crevices around the outside of your home.
Formosan termites
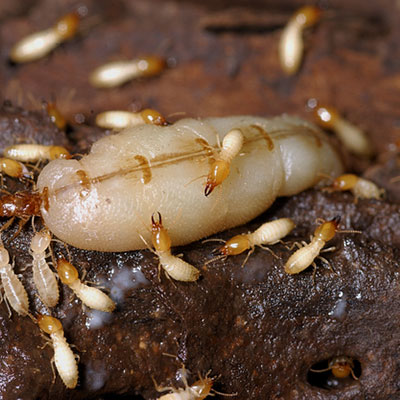
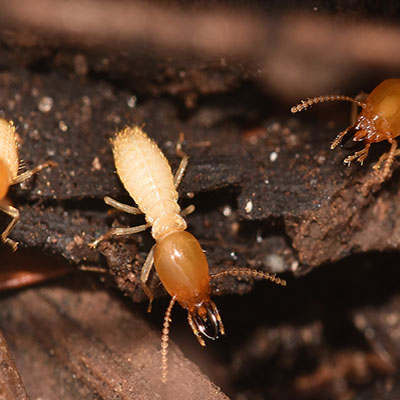
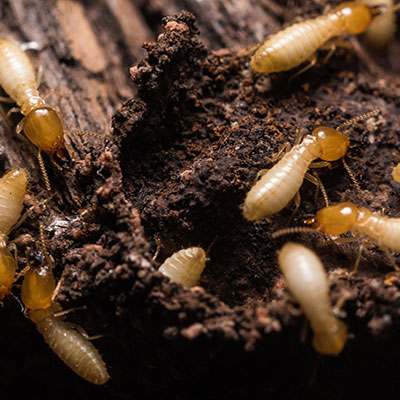



Formosan termite colonies can be up to 300 feet long and there can be tens of thousands of termites in a single colony. Formosan termite colonies are divided into three groups: workers, soldiers and reproductives. They are the largest and most destructive kind of termite. Formosan Termites eat wood and fabric made from plants. When they eat dead trees, these termites help the environment and make space for new plant life. Formosans live in huge underground colonies, and build mud nests inside the walls of a building. They can also live in boats and buildings. To avoid Formosan termites, make sure water drains away from your house and keep damp wood away from your home.
Subterranean Termites
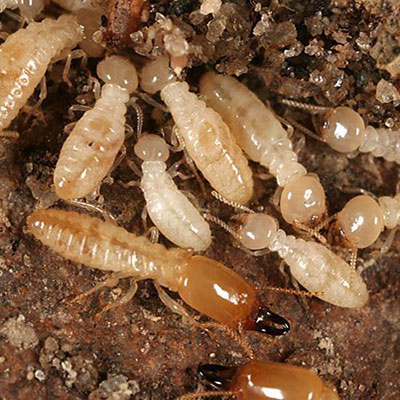
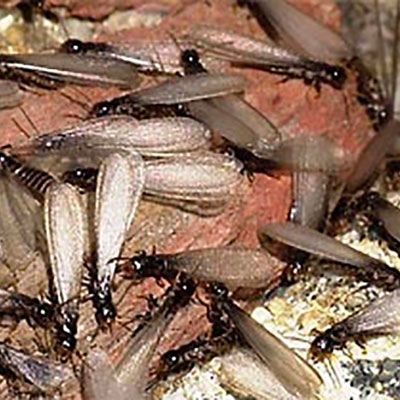
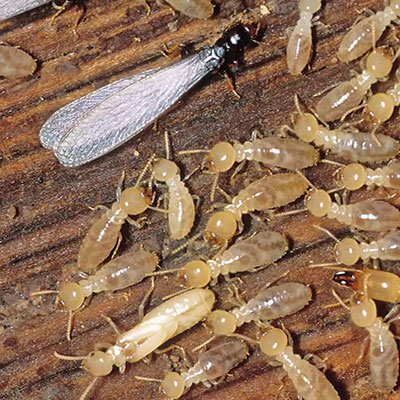



Subterranean Termite colonies can have up to 2 million members! Their colonies are divided into three groups: workers, soldiers and reproductives. Termites eat wood, wallpaper, plastics and fabric made from plants. Subterranean termites need contact with the soil to survive. They live in underground colonies or in wet areas aboveground. They build tunnels to reach food and every spring, groups of reproductive termites fly off to start new colonies. Subterranean termites are the most destructive kind of termite. They can eat a lot of wood and they can cause a lot of expensive damage to a house! They can destroy building foundations, wooden support beams, plastic plumbing pipes, sub-flooring, insulation ? even swimming pool liners and filtration systems! Termites can also injure or destroy living trees and shrubs. To Prevent your house from Subterranean Termites Don?t let water pool around your home's foundation. Termites like that! Never leave wood scraps in the yard for them to snack on.
Cockroaches
German Cockroach
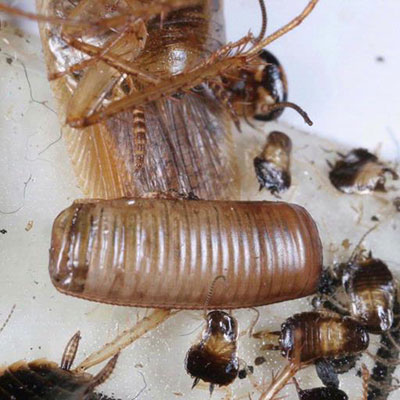
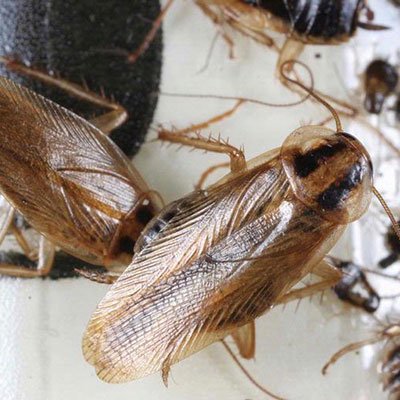
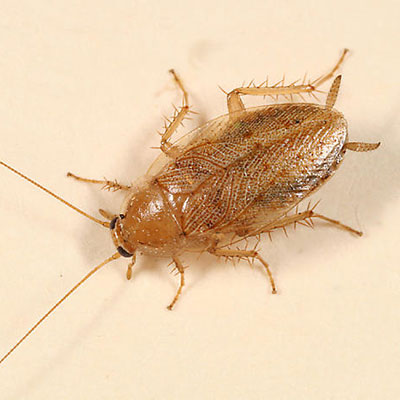



The German cockroach is 12 to 17 mm (1/2 to 5/8 inch) long, tan to light brown, and has two dark brown stripes on the body region (pronotal shield) just behind the head. Females will produce four to eight egg capsules during their lifetime, with each capsule containing approximately 40 eggs. The egg capsule is retained by the female until the eggs are ready to hatch, usually in 28 to 30 days.
German cockroaches are widespread and can be found in homes, restaurants, hospitals, nursing homes or apartments. Within these areas, the cockroaches prefer sites close to moisture and food, making them common pests in kitchens, bathrooms and food-storage areas. Of the cockroaches which infest structures, the German cockroach is probably found more frequently than other species.
American Cockroach
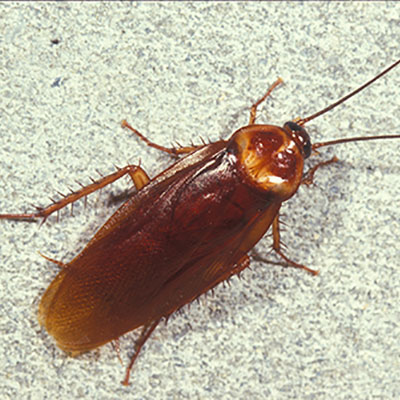
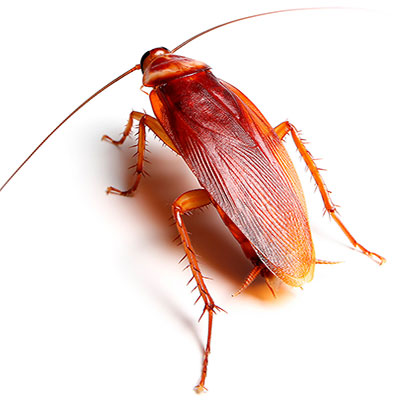
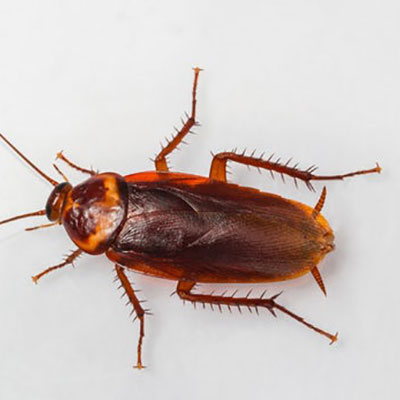



The American cockroach is one of the largest cockroaches in the Northeast. It is about 40 mm (1.5 inches) long with a reddish-brown body. The center portion of the pronotal shield is light brown, while the outer edges are yellow. Even though both sexes are winged, their flight is more of a gliding movement from point to point than active flight.
The female American cockroach will not retain the egg capsule for more than a day after its formation, instead dropping the capsule in some suitable site. Under some conditions it may be glued to a surface. The number of capsules produced by a female will range from 6 to 14, with each capsule con taining 14 to 16 eggs. The eggs hatch in 50 to 55 days. The American cockroach prefers dark, moist sites where it feeds on decaying organic matter. Such sites include basements, kitchens, clothes hampers, drains, bathroom plumbing or sewers. High populations have been known to develop in sewers, from where they infest households or other structures.
Brownbanded Cockroach
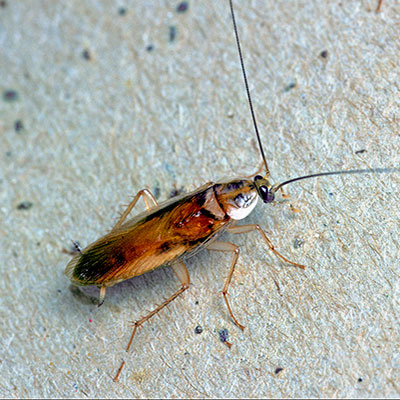
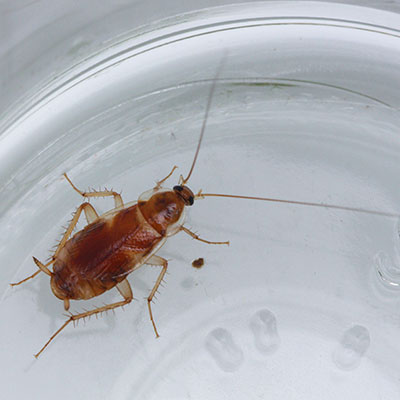
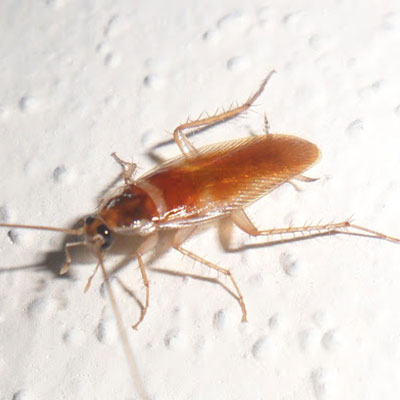



The brownbanded cockroach is 12 mm (1/2 inch) long, light brown, and has two lighter colored bands running across the body. These bands are located at the base of the wings and on the abdomen. The bands are much darker during the immature stages. The brownbanded female carries the egg capsule for 24 to 48 hours before gluing it to a surface. The capsule contains approximately 18 eggs that hatch in 50-74 days. An adult female produces about 18 egg capsules over a life-span of 10 months.
The brownbanded cockroach requires less moisture than other cockroaches. It is more prevalent in homes, apartments, hotels and hospital rooms than in restaurants or stores. Evidence of this cockroach may be found behind pictures, in furniture, the underside of chairs and tables, upper kitchen cabi nets or the upper shelves of closets and pantries. The brownbanded cockroach often infests electrical appliances such as radios, televisions, telephones and computers.
Bed bugs
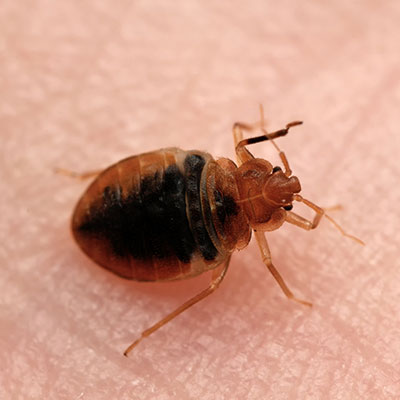
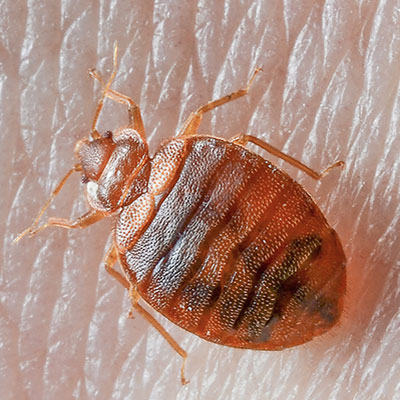
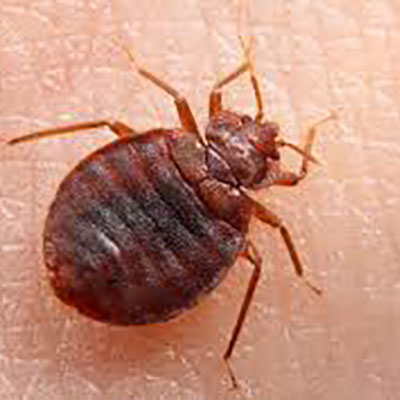



Bed bugs belong to the family Cimicidae and class insecta. They are flat, oval and wingless. These are reddish-brown bugs that are usually less then 7mm long, have moderately long, slender antennae, thin legs and vestigial wings in the form of stubs. Females can deposit one to five eggs a day, and may lay 200 to 500 eggs in a lifetime. Under normal room temperatures and with an adequate food supply, bed bugs can live over 300 days.
They can run surprisingly fast. They are found in human habitations, particularly bedrooms and feed upon human blood. Lacking human blood, this insect will feed on the blood of rats, mice, rabbits or chickens. It can survive without food for up to 15 months. The bed bug is not known to transmit any human diseases. Bed bugs were brought to North America by early colonists. Elimination of bed bugs from a structure is unlike any other pest control challenge. It requires joint efforts of the client and the pest management expert. Through preparation of the site by the client, a thorough inspection, precise and targeted treatment of the bug harborage sites are the key to successful bed bug control.The bed bug is not known to transmit any human diseases. Bed bugs were brought to North America by early colonists. Elimination of bed bugs from a structure is unlike any other pest control challenge. It requires joint efforts of the client and the pest management expert. Through preparation of the site by the client, a thorough inspection, precise and targeted treatment of the bug harborage sites are the key to successful bed bug control.
Rodents
Rats
An adult rat can squeeze into your home through a hole as small as the size of a quarter. Rats can live for up to 18 months, but most die before they are one year old. They have strong teeth that allow them to chew through glass, cinderblock, wire, aluminum and lead. Smell, taste, touch and sound help direct them to their food sources.
Rats are also responsible for spreading Bubonic Plague, also known as the "Black Death". Although fleas are primarily responsible for infecting humans, they were originally infected with the plague by feeding on the blood of rats.
Norway Rat
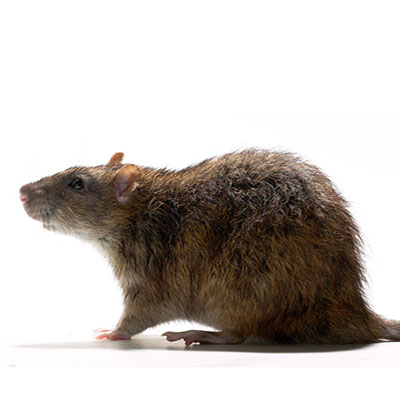
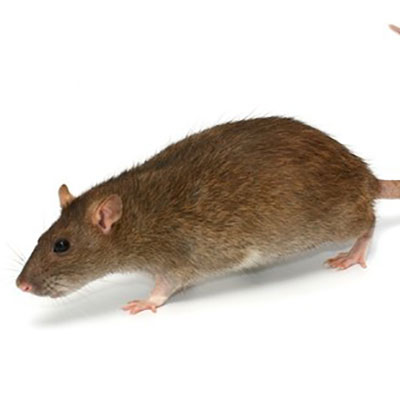
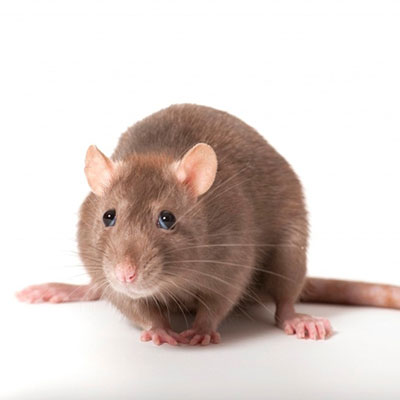



Norway rats eat a wide variety of foods but mostly prefer cereal grains, meats, fish, nuts, and some fruits.
When Norway rats invade buildings, they usually remain in the basement or ground floor. They also live in fields, farms, woodpiles and buildings. Their nests are usually lined with shredded paper or cloth. These rats are known for the damage they cause by chewing on materials, urinating on food and eating stored foods. They have also been known to chew on wires, which can cause fires to start. They also carry disease and ectoparasites. Rats will also attack both animals and humans. Human babies and even adults have been killed in rat attacks.
Roof Rat
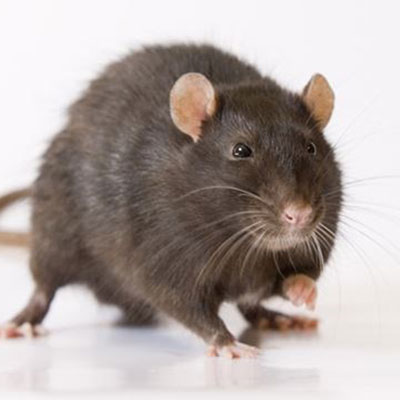
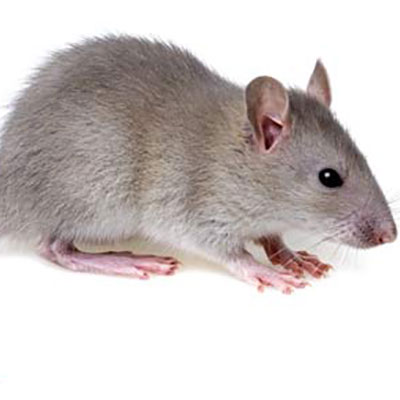
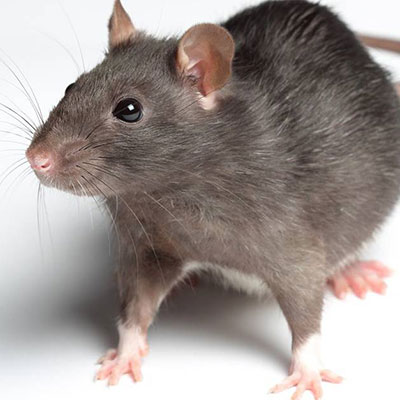



Roof Rats are excellent climbers and get their name because they usually live high off the ground, like on the roof of a building. They have very poor vision and are color blind, but they have extremely strong senses of hearing, smell, touch and taste. Rats have four to six litters a year and each litter has 6 to 12 babies in it. These rats are only pregnant for about 21 to 23 days and they can start reproducing when they are three months old. Roof Rats prefer eating fruits, berries, vegetables, cereal, pet food, nuts, grain, slugs, snails and rotten food.
Roof Rats are excellent climbers and they usually live in spaces on the tops of buildings, on roofs or in attics. They also live in sheds, garages, boxes, ceilings, under floors, in wood heaps and in thick grass.Roof rats cause damage to structures by chewing, eating stored foods and carrying diseases, such as Hantavirus. They are most famous for spreading the highly contagious bubonic plague in the Middle Ages. Rats will also attack both animals and humans. Human babies and even adults have been killed in rat attacks.
House Mouse
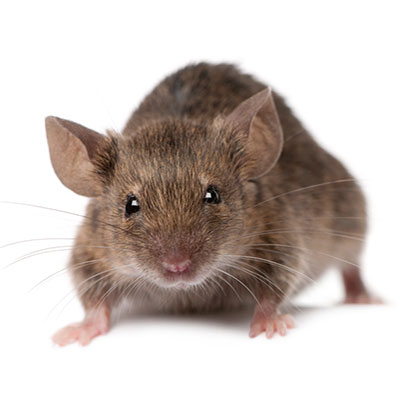
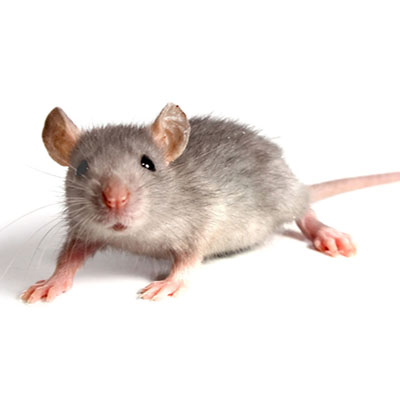
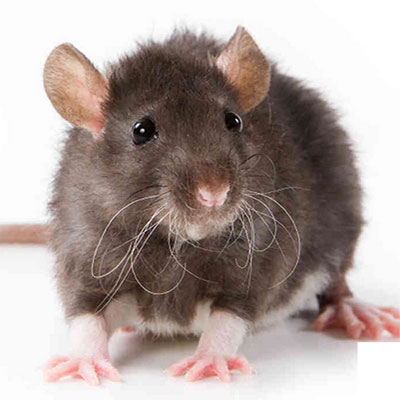



The House Mouse makes its own nest but lives in groups, sharing escape holes and common areas for eating, urinating, and defecating. It takes turns grooming its fellows, especially on the head and back, where it is difficult for the animal to groom itself. If the population grows too dense, many females, particularly adolescents, become infertile. A highly migratory existence and rapid rate of reproduction enable the House Mouse to thrive; it takes advantage of situations not readily available to other species, including cultivated fields, which offer a rich if temporary habitat. As a crop develops, the mice move in and have several litters in quick succession, building large populations quickly; when the field is harvested or plowed, they move out. Many perish, many find other fields, and still others invade buildings. Sometimes these migrations assume plague proportions: In 1926?1927, an estimated 82,000 mice per acre (202,000 per ha) wreaked havoc in the Central Valley of California. In such densities, House Mice, though generally timid, have been known to run over people?s feet and even to bite. These mice eat or their droppings contaminate large quantities of grain and other valuable foodstuffs. Their scientific name derives from the Sanskrit musha, meaning "thief." They chew or shred anything chewable or shreddable, including furniture and wires, and sometimes start fires. They can scurry up rough vertical walls and even pipes; they gnaw holes in walls, floors, and baseboards. Like Black and Norway rats, House Mice can spread disease. In the wild, birds and mammals are predators. Centuries ago, cooked mouse meat was a folk remedy for colds, coughs, fits, and fevers, but it is not recommended today. The white mice used in research laboratories are albinos bred from this species.
Deer Mice
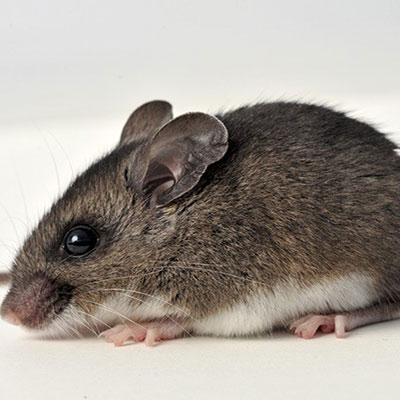



The deer mouse rarely invades homes, and is found in rural areas. The deer mouse makes its home outdoors in sheltered areas such as hollow tree logs or piles of debris. On the rare occasions the deer mouse comes indoors, it prefers undisturbed areas such as attics. The deer mouse transmits the potentially fatal Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome. The disease can be transmitted through contact with mouse carcasses, or by breathing in aerosolized urine droplets of infected deer mice.
Ants
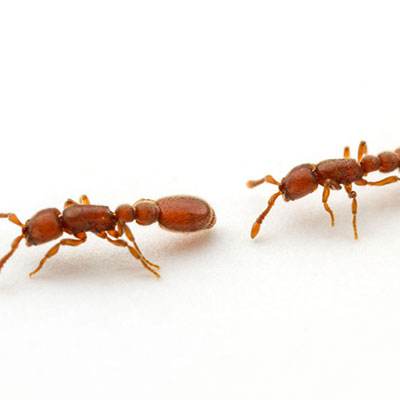
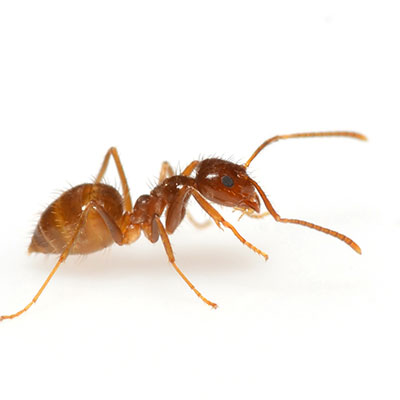



Ants have been living on the Earth for more than 100 million years and can be found almost anywhere on the planet. It is estimated that there are about 20,000 different species of ants. For this reason ants have been called Earth's most successful species.
Ants build many different types of homes. Many ants build simple little mounds out of dirt or sand. Other ants use small sticks mixed with dirt and sand to make a stronger mound that offers protection from rain. Western Harvester ants make a small mound on top, but then tunnel up to 15 feet straight down to hibernate during winter. Ant mounds consist of many chambers connected by tunnels. Different chambers are used for nurseries, food storage, and resting places for the worker ants. Some ants live in wood like termites. Army ants don't make a home at all but travel in large groups searching for food. Sociology: Ants are social insects, which means they live in large colonies or groups. Some colonies consist of millions of ants. There are three types of ants in each species, the queen, the sterile female workers, and males. The male ants only serve one purpose, to mate with future queen ants and do not live very long. The queen grows to adulthood, mates, and then spends the rest of her life laying eggs. A colony may have only one queen, or there may be many.
Mosquito
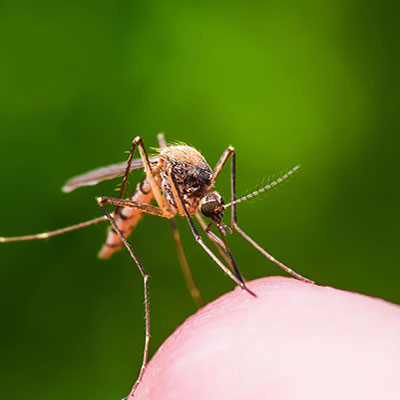
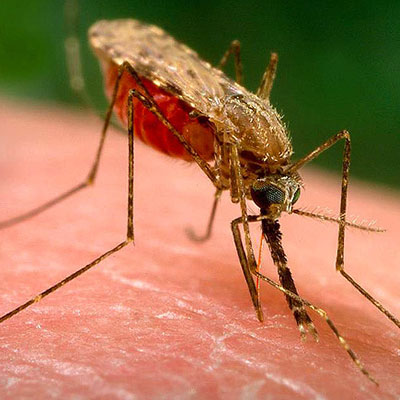


Not all mosquitoes are important disease carriers, even though most suck the blood of man and other vertebrate animals. Only the female mosquito bites. They require standing or slow moving water in which to develop, and breed in fish ponds, unattended swimming pools, and rain puddles. Treatment and Control: Mosquito control begins with an accurate and thorough inspection of the target area and surrounding areas. Dewey Integrated Pest Management (DIMP) 5-step program will significantly reduce mosquito population from around the structure.
Flies
Fruit Fly
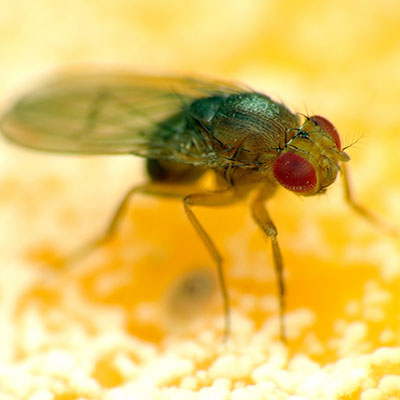
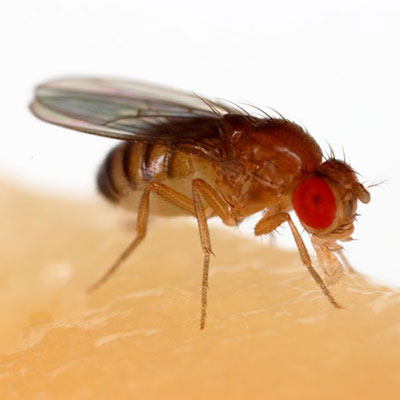



Fruit flies develop by complete metamorphosis. The eggs (which are difficult to see with the naked eye) are deposited near the surface of fermenting fruit or organic matter. A pair of filaments that are attached to the eggs protrude above the surface of the liquid. The female fruit fly will lay about 500 eggs. The larvae emerge about 30 hours after the eggs have been laid and feed near the surface of the fermenting material. The larvae feed for five to six days then crawl to drier areas of the food source or even out of the food source to pupate. The larva transforms into the pupa in the last larval skin, or puparium, which bears a conspicuous pair of filaments on the anterior end.
The adult fruit fly emerges several days later. The newly emerged fruit flies are attracted to light and become sexually active in about two days. The adults mate more than once. Under ideal conditions, the life cycle from egg to adult can be completed in as little as eight days. The sudden appearance of large populations is not uncommon inside buildings. When searching for fruit fly breeding sources, remember that the larva can only survive in decaying organic matter that is moist. The first obvious place to check is where any fruits or vegetables or stored outside of refrigerators or coolers. Other areas to inspect would be recycling bins, seldom used (or cleaned) garbage cans, underneath and behind large appliances. Do not overlook drains where small flies are often found breeding in the super thin layer or film of debris that naturally accumulates in pipes, traps and drains.
House Fly
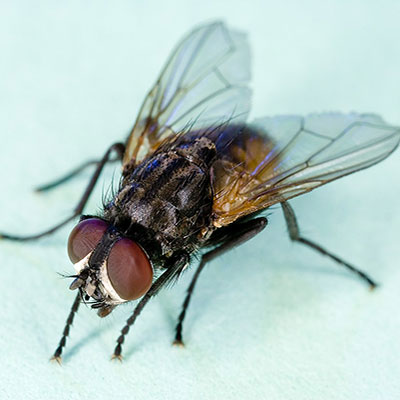
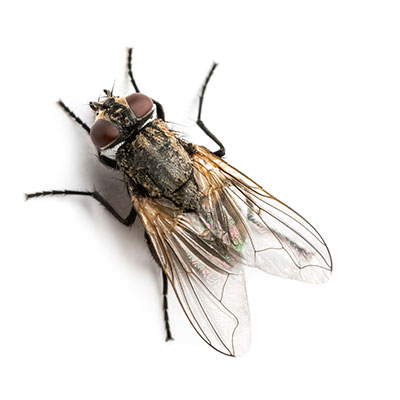
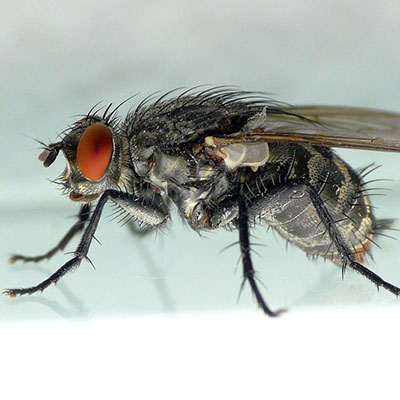



The house fly passes through four stages in its life cycle: egg, larva, pupa and adult. The female of the species can be seen depositing their eggs on suitable breeding materials. Often, the females can be seen in clusters of up to 50 individuals. The female house fly lays individual eggs that pile up in masses of 75 to 150 eggs; in her lifetime, a single female house fly may lay up to 900 eggs. The female fly begins laying her eggs anywhere from 4 to 12 days from emerging from her pupae. She may lay 5 or 6 batches at intervals of several days between each. Your inspection should begin outside the home or building; although house flies are known to breed in indoor dirty trash cans, they are usually found feeding and breeding in fresh manure, rotting fruits and vegetables, damp garbage and damp, decaying organic materials that are located outside of the structure. After locating all possible breeding sites, look for areas where house flies enter a structure. Cracks around windows, doors and vents are the usual culprits.
Phorid Flies
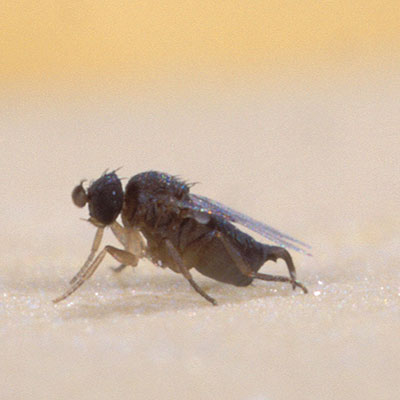
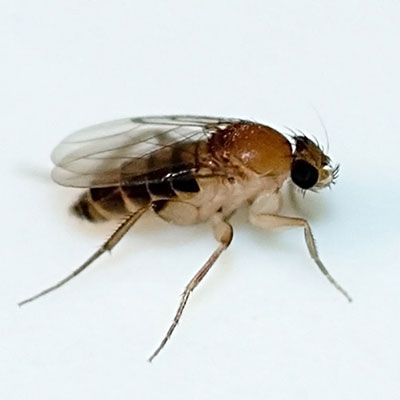
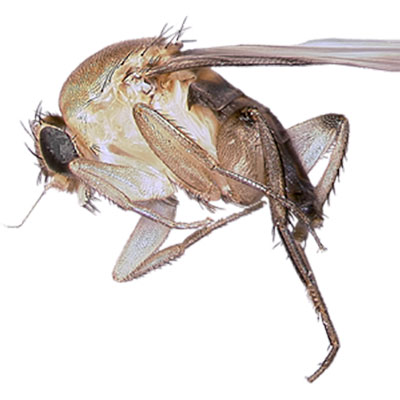



When searching for Phorid fly breeding sources, remember that the larva can only survive in decaying organic matter that is moist. The first obvious place to check is where any fruits or vegetables or stored outside of refrigerators or coolers. Other areas to inspect would be recycling bins, seldom used (or cleaned) garbage cans, underneath and behind large appliances. Do not overlook drains where small flies are often found breeding in the super thin layer or film of debris that naturally accumulates in pipes, traps and drains.
Phorid flies develop by egg, larva, pupa and adult. The female will lay about 20 eggs at a time and will lay about 40 eggs in a 12 hour period. Each adult female phorid will lay approximately 500 eggs. The tiny eggs are deposited on or near the surface of decaying organic matter. Larvae emerge in 24 hours and feed for 8 to 16 days. The Phorid fly larvae then crawl to a drier spot to pupate. The life cycle from egg to adult can be completed in as little as 14 days (under ideal conditions) but may take as long as 37 days to complete their cycle.
The phorids, also known as humpbacked flies, are small to minute flies that resemble fruit flies in appearance. The Phorid fly lacks the red eye color that is the classic trademark of the fruit fly. Phorid flies are in the small category of flies, measuring up to 1/8 inch in length, including the wings. The most prominent feature of this fly is the humpbacked shape of its thorax. The severe arch of the thorax gives it the common nickname of humpbacked fly. The most easily recognized feature (seen with the naked eye) is the habit of the adult Phorid fly running rapidly across surfaces instead of immediately flying when disturbed. Most flies immediately take flight.
Phorid flies are also know as coffin flies, when found in mortuaries and mausoleums.
Bees
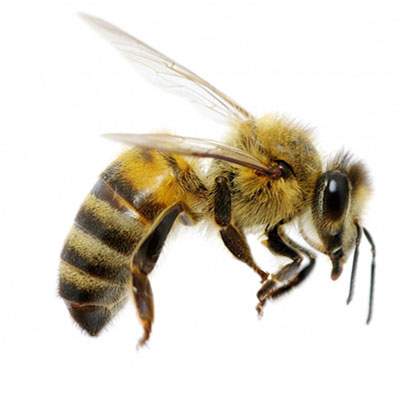
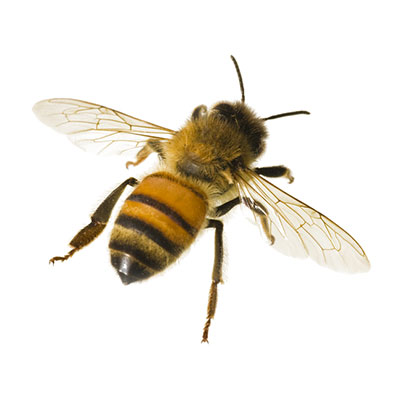
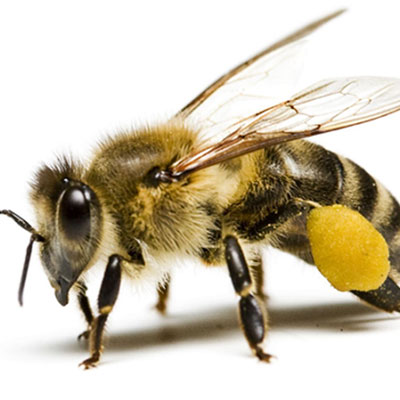



The bee pollinates fruit trees, flowers, and plants to make honey to feed the colony. Bees can create a hive or swam (sometimes as many as 50,000 bees) in a rafter, shed, tree, or bush. Bee stings can be deadly to infants, the elderly, and persons allergic to bee venom. Bees are beneficial insects, however if their nest is located in or close to an occupied structure, then control is warranted. Live removal of honeybees is desirable. If honeybees must be killed in a wall void or attic, pesticide application should be made at night using only background light.
Pigeon
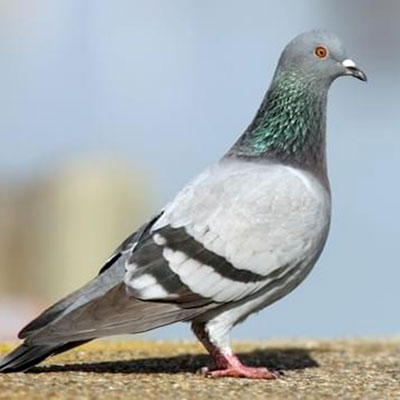
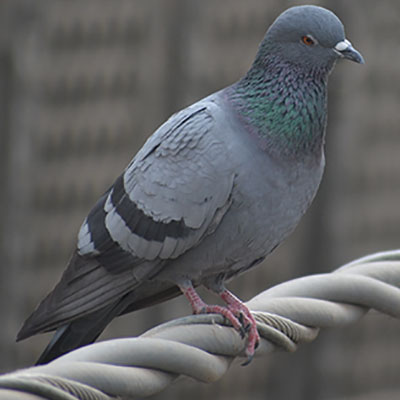
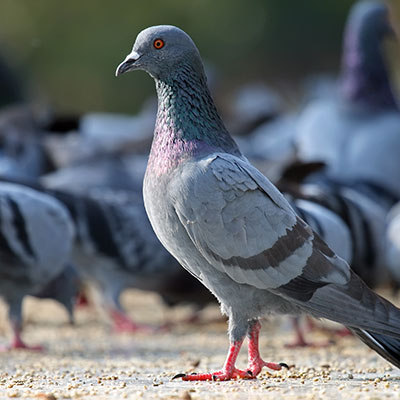



Pigeons often prefer to use the interior portions of buildings to nest and roost if an opportunity for access is provided. Openings to lofts, steeples, vents, and eaves can be blocked with 1/2-inch galvanized wire mesh, wood, sheet metal, or other solid construction materials to prevent pigeons from entering. Controlling pigeons on the exterior surfaces of buildings often requires considerably more effort. The most effective and permanent methods of control involve structural modifications which either physically exclude pigeons from the preferred surface or make it difficult for the birds to rest comfortably on the exposed building surfaces. Physical exclusion can be accomplished by installing weather resistant netting, wire screening, sheet metal, or other materials in a manner that will restrict access to the roosting sites. A grid of heavy gauge monofilament line spaced at six-inch intervals may also be used to create a fence that will interfere with the birds' normal flight pattern to the roosting area.
Silverfish
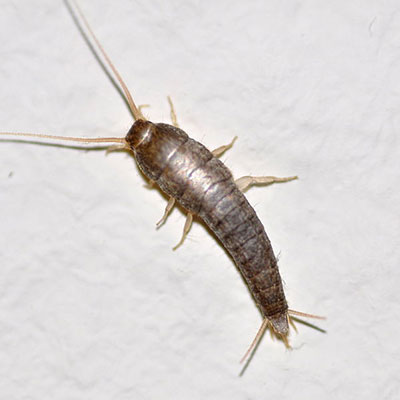
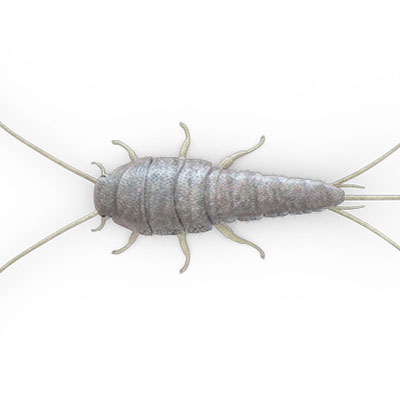
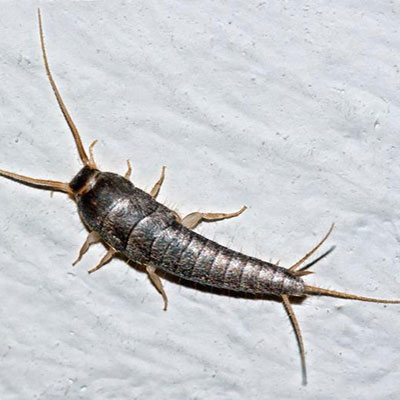



Silverfish like to eat starch in wallpaper and book bindings, and also starch found in laundered clothing. They live in walls that are wallpapered, dens and libraries, closets, and storage areas. Treatment and Control: Our 5-step principles will produce excellent control of silverfish in a structure.
Ticks
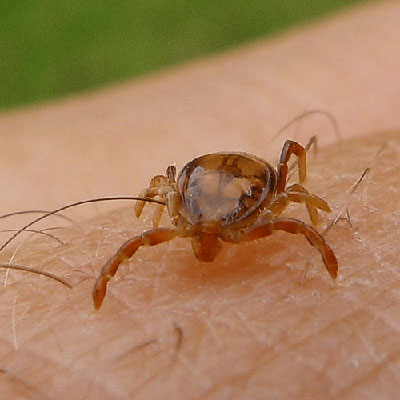
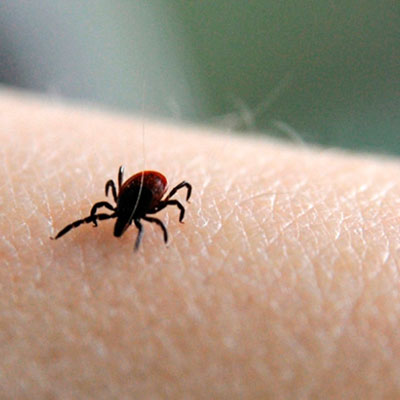
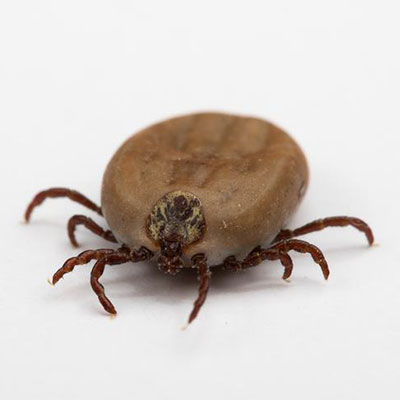



Ticks are blood feeding external parasites of mammals, birds, and reptiles throughout the world. Approximately 850 species have been described worldwide (Furman and Loomis 1984). There are two well established families of ticks, the Ixodidae (hard ticks), and Argasidae (soft ticks). Both are important vectors of disease causing agents to humans and animals throughout the world. Ticks transmit the widest variety of pathogens of any blood sucking arthropod, including bacteria, rickettsiae, protozoa, and viruses. Some human diseases of current interest in the United States caused by tick-borne pathogens include Lyme disease, ehrlichiosis, babesiosis, rocky mountain spotted fever, tularemia, and tick-borne relapsing fever.
Snake
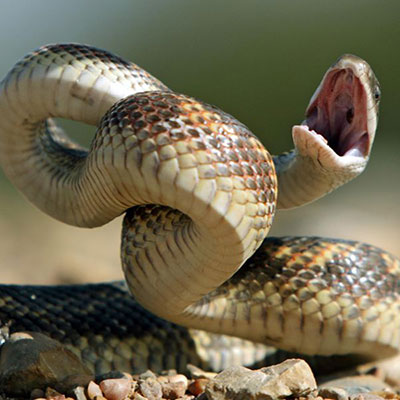
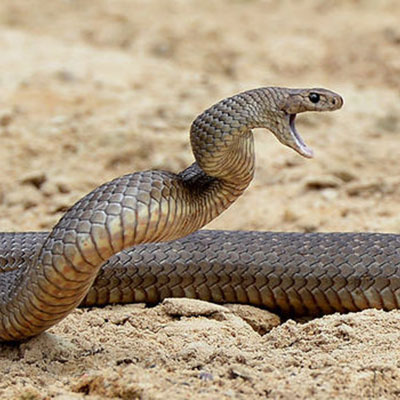
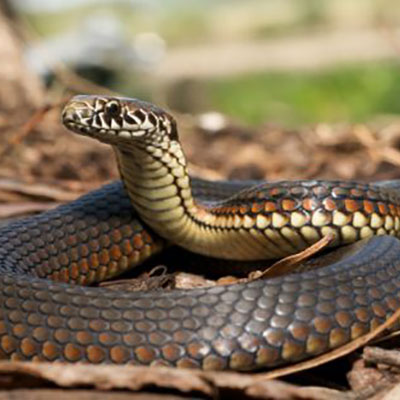



As eaters of many pest species, snakes can be very helpful around the yard. Since most snakes find their way onto your property because they are following food, a persistent snake problem may mean that there are other pests, such as mice, rats, crickets, or cockroaches, in your home. Trapping and animal control specialists are the primary means of snake control in areas where snakes are rare. Exclusion, habitat modification, and biological control strategies are more effective in areas where snakes are common.
Keeping Snakes Away
Lawn care: Mow and trim your lawn regularly. Snakes like to hide in cool, damp, shaded areas, and taller grasses offer more protection to snakes and natural predators Controlling other pests: Controlling insect and rodent populations on your property can be difficult, but it will help keep snakes out of your yard. If there is no food on your property, snakes will go elsewhere.